Overview
One of the coolest things about a beautiful UI/UX is the transitions. When I started out in web, I used to find interesting animations in javascript and css and try to recreate it. I feel the same about mobile. Transitions between views is very important and can distinguish your app from the millions of others. Make sure to check out jTribe’s post as it contains everything from this post and more.
Content
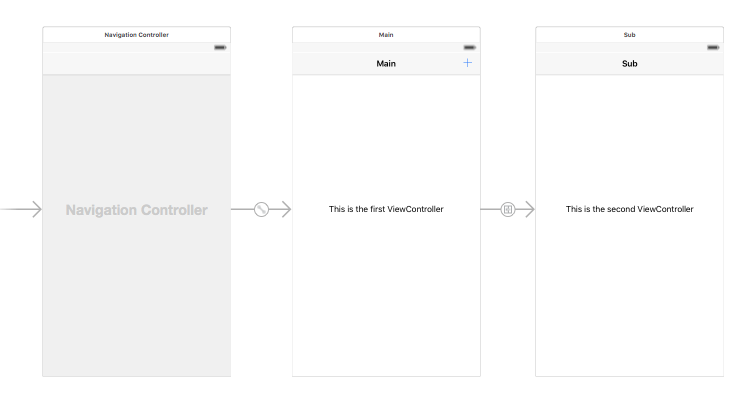
We’re going to create the following effect when we interact with a NavigationController.

We’re going to create two classes: CustomInteraction and CustomPresentation.
In XCode go to File -> New -> File -> Source -> Swift file.
CustomInteraction
Attaches to a navigation controller and listens for a gesture (we override default return gesture)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
import UIKit
class CustomInteraction: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition {
var navigationController: UINavigationController?
var shouldCompleteTransition = false
var transitionInProgress = false
override init() {}
func attachToViewController(viewController: UIViewController) {}
private func initializeGestureRecognizer(view: UIView) {}
func handlePan(gestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer) {}
func handlePan(gestureRecognizer: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {}
func handlePanBegan(location: CGPoint) {}
func handlePanChanged(viewTranslation: CGPoint) {}
func handlePanCancelled(gestureRecognizer: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {}
}
enum PercentageValues: CGFloat {
case Threshold = 50.0
case Half = 0.50
}
Here’s the breakdown of each method.
-
attachToViewController: Attaches theCustomInteractionto anUIViewController. Usually, this is the top view (NavigationController) so that you only need to attach it once. -
initializeGestureRecognizer: This overrides the default UIPanRecognizer from Apple which lets you swipe to the left instead of pressing the back button.
Now let’s add all the rest of the code for this class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
mport UIKit
class CustomInteraction: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition {
var navigationController: UINavigationController?
var shouldCompleteTransition = false
var transitionInProgress = false
override init() {
super.init()
completionSpeed = 1 - percentComplete
}
func attachToViewController(viewController: UIViewController) {
navigationController = viewController.navigationController
initializeGestureRecognizer(viewController.view)
}
private func initializeGestureRecognizer(view: UIView) {
view.addGestureRecognizer(UIPanGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: "handlePan:"))
}
func handlePan(gestureRecognizer: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
guard let gestureSuperview = gestureRecognizer.view?.superview else { return }
let viewTranslation = gestureRecognizer.translationInView(gestureSuperview)
let location = gestureRecognizer.locationInView(gestureSuperview)
switch gestureRecognizer.state {
case .Began:
handlePanBegan(location)
case .Changed:
handlePanChanged(viewTranslation)
case .Cancelled, .Ended:
handlePanCancelled(gestureRecognizer)
default:
break
}
}
func handlePanBegan(location: CGPoint) {
if location.x > PercentageValues.Threshold.rawValue {
cancelInteractiveTransition()
return
}
transitionInProgress = true
navigationController?.popViewControllerAnimated(true)
}
func handlePanChanged(viewTranslation: CGPoint) {
// xValueReached has to be [0.0, 1.0]
let xValueReached = CGFloat(fminf(fmaxf(Float(viewTranslation.x / 200.0), 0.0), 1.0))
shouldCompleteTransition = xValueReached > PercentageValues.Half.rawValue
updateInteractiveTransition(xValueReached)
}
func handlePanCancelled(gestureRecognizer: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
transitionInProgress = false
if !shouldCompleteTransition || gestureRecognizer.state == .Cancelled {
cancelInteractiveTransition()
} else {
finishInteractiveTransition()
}
}
}
enum PercentageValues: CGFloat {
case Threshold = 50.0
case Half = 0.50
}
CustomPresentation
Animation that is performed when transitioning. We attach this to the navigation controller.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import UIKit
import Foundation
class CustomPresentation: NSObject, UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning {
private let scale = UIScreen.mainScreen().scale
private let identity = CATransform3DIdentity
private var distance: CGFloat {
return ZPositions.Distance.rawValue
}
private var spatial: CGFloat {
return ZPositions.Spatial.rawValue
}
var reverse: Bool = false
func transitionDuration(transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning?)
-> NSTimeInterval {}
func handleAnimationFinish(transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning,
toView: UIView, fromView: UIView) {}
func animateTransition(transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning) {}
func rasterize(withLayer layer: CALayer) {}
func addDepthDownToAnimation() -> CATransform3D {}
func addDepthDownFromAnimation() -> CATransform3D {}
}
enum ZPositions: CGFloat {
case Spatial = 300
case Distance = 150
}
Here’s the breakdown of each method.
-
transitionDuration: How long the transition will take. -
animateTransition: What the animation will be. (most of the code is here) -
rasterize: Makes the animation display match the resolution of the device. -
addDepthDownToAnimation: This is where the transition happens, it actually uses the Z-axis to animate and adds depth. Without this, you wouldn’t see the animation.
Now let’s add all the rest of the code for this class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
import UIKit
import Foundation
class CustomPresentation: NSObject, UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning {
private let scale = UIScreen.mainScreen().scale
private let identity = CATransform3DIdentity
private var distance: CGFloat {
return ZPositions.Distance.rawValue
}
private var spatial: CGFloat {
return ZPositions.Spatial.rawValue
}
var reverse: Bool = false
func transitionDuration(transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning?)
-> NSTimeInterval {
return 2.0
}
func handleAnimationFinish(transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning,
toView: UIView,
fromView: UIView) {
if transitionContext.transitionWasCancelled() {
toView.removeFromSuperview()
toView.layer.removeAllAnimations()
} else {
fromView.removeFromSuperview()
fromView.layer.removeAllAnimations()
}
transitionContext.completeTransition(!transitionContext.transitionWasCancelled())
}
func animateTransition(transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning) {
let containerView = transitionContext.containerView()
let toViewController = transitionContext
.viewControllerForKey(UITransitionContextToViewControllerKey)!
let fromViewController = transitionContext
.viewControllerForKey(UITransitionContextFromViewControllerKey)!
let toView = toViewController.view
let fromView = fromViewController.view
// add animation to view
toView.layer.transform = addDepthDownToAnimation()
// initially hide view and rasterize
toView.alpha = 0.0
rasterize(withLayer: toView.layer)
// add both subviews and show only one of them depending on reverse
containerView?.addSubview(toView)
containerView?.addSubview(fromView)
containerView?.sendSubviewToBack(reverse == true ? fromView : toView)
// change zPosition depending on which view should be displayed
fromView.layer.zPosition = reverse ? -spatial : spatial
toView.layer.zPosition = reverse ? spatial : -spatial
UIView.animateWithDuration(transitionDuration(transitionContext),
delay: 0.0,
options: .CurveEaseOut,
animations: { [weak self] in
guard let weakSelf = self else { return }
// add animation
fromView.layer.transform = weakSelf.addDepthDownFromAnimation()
// initially hide view and rasterize
fromView.alpha = 0.0
weakSelf.rasterize(withLayer: fromView.layer)
// reset transform
toView.layer.transform = CATransform3DIdentity
toView.alpha = 1.0
}, completion: { finished in
self.handleAnimationFinish(transitionContext,
toView:toView,
fromView:fromView)
})
}
func rasterize(withLayer layer: CALayer) {
layer.contentsScale = scale
layer.shouldRasterize = true
layer.rasterizationScale = scale
}
func addDepthDownToAnimation() -> CATransform3D {
let toViewZ: CGFloat = reverse ? distance : -distance
var rotationAndPerspectiveTransform: CATransform3D = CATransform3DIdentity
rotationAndPerspectiveTransform.m34 = 1.0 / -500.0
rotationAndPerspectiveTransform = CATransform3DTranslate(
rotationAndPerspectiveTransform, 0.0, 0.0, toViewZ)
return rotationAndPerspectiveTransform
}
func addDepthDownFromAnimation() -> CATransform3D {
let fromViewZ: CGFloat = reverse ? -distance : distance
var rotationAndPerspectiveTransform: CATransform3D = CATransform3DIdentity
rotationAndPerspectiveTransform.m34 = 1.0 / -500.0
rotationAndPerspectiveTransform = CATransform3DTranslate(
rotationAndPerspectiveTransform, 0.0, 0.0, fromViewZ)
return rotationAndPerspectiveTransform
}
}
enum ZPositions: CGFloat {
case Spatial = 300
case Distance = 150
}
Storyboard
This is what your storyboard looks like.
To use the two classes that we created, add them at the top of your MainViewController class.
Make sure your MainViewController implements UINavigationControllerDelegate.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
import UIKit
class MainViewController: UIViewController, UINavigationControllerDelegate {
let presenting = CustomPresentation()
let interaction = CustomInteraction()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
navigationController?.delegate = self
}
func navigationController(navigationController: UINavigationController,
animationControllerForOperation operation:
UINavigationControllerOperation,
fromViewController fromVC: UIViewController,
toViewController toVC: UIViewController) ->
UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
if operation == .Push {
interaction.attachToViewController(toVC)
}
presenting.reverse = operation == .Pop
return presenting
}
func navigationController(navigationController: UINavigationController,
interactionControllerForAnimationController animationController:
UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) ->
UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
return interaction.transitionInProgress ? interaction : nil
}
}